To fill a glaring gap in the decommissioning market, Voll Marintek Limited is pioneering the HWU-150 Lean Machine, a dual jack lifting system with key advantages over rigless operations and MDR to deliver significant cost, risk and climate benefits for the industry.
Dennis Vollmar, CEO of Voll Marintek Limited, spoke to Offshore Network to discuss his innovative solution in detail and explained how he identified this opening in the market.

“So we realised there was a gap by knocking on doors really. We had deep interactions with different operators, service providers and contractors and realised there was space for something new.
“It comes down to knowing well conditions. Wells which are coming to the end of their life are usually decades old and in this time the way data is collected has changed. In many cases you don’t even know which revision is the most updated one. In these cases, you have two options: either a customised approach with the deployment of specialised workover units for each subtask or use a rig.”
There are drawbacks to both. In the former, rigless workover units require intensive planning, a detailed knowledge of well integrity and, due to their simplicity and dependency on crane support, they are highly vulnerable to unforeseen events and weather conditions. Rigs on the other hand have more capacity and can simplify the planning and execution phase, but generally have a very high spread cost and carbon footprint.
Voll Marintek, therefore, has developed the Lean Machine, a multipurpose unit to fill the void between these two options.
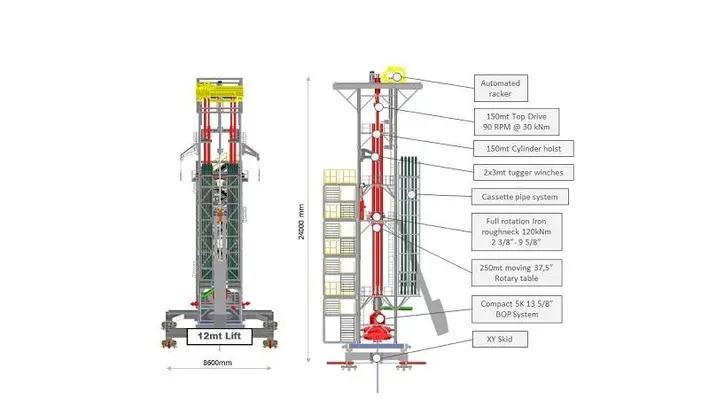
“The Lean Machine is basically a hybrid solution between a hydraulic workover unit (HWU) and a modular drilling rig (MDR). It combines the main features of a HWU such as fast assembly, lightness, compactness and only requires a small footprint in addition to the benefits of MDR such as drilling, milling, making pipe connections respectively handling different pipe types conventionally and in a safe manner.”
The dual jack lifting system is a modular adaptable multipurpose unit which has the capacity to be upgraded with additional features so that it can be customised for each project and adapted to various interfaces. It consists of different modules designed to cover a specific P&A task which can be stacked on top of each other, extending the previous operational envelope of the complete system (this is called ‘The Happy Meal’). This means it can be upgraded with existing modules at the offshore location to perform sequential tasks instead of mobilising specialised equipment for each subtask or oversized workover rigs.

The operator can choose the options required based on additional costs for each contingency as desired always keeping integrated costs in mind. Importantly, the compactness of the 10 ft container footprint and the lightness of each module (around 12 mt) allow its assembly on a skid beam substructure, heave compensation platform or in a derrick structure of an existing rig.
Explaining the benefits of the system, Vollmar commented, “Cost and risk are the main drivers here. When looking at costs for an operation you want to see exactly the expenditure that will be incurred. Often this is not possible without an extensive preparation phase and even then unforeseen circumstances can occur – which is why rigs are often used.
“What we are doing is to see how we can make the whole process lean. So when you know the potential work scopes you need to perform you can configure the machine to it but, if you have the eventuality of making adaptations (maybe to enhance the operational envelope or even downsize it), you can do that in the field and this is where costs can be significantly reduced.”
Vollmar claimed that the deployment of the modular adaptable unit to tackle challenges within the P&A and decommissioning space will enable the highest potential cost savings available. The faster pipe recovery system alone allows cost savings of US$1mn per well based on a five day execution phase reduction. A global operator has already performed a preliminary total cost analysis in comparison to conventional solutions and identified a cost reduction above 30% for his 100 well campaign.

The high cost of a rig is also mirrored in its high carbon footprint, a somewhat neglected but increasingly pressing concern for the oil and gas industry. HWU’s of course have an advantage here, but poor weather, unforeseen events and the mobilisation of additional equipment to cover all P&A phases can bring down operational efficiency and extends the time duration for a P&A campaign– which is not a problem for the Lean Machine.
Mounting market interest
While still at the start of its journey, the Lean Machine is already attracting attention and suitors which is driving it steadily towards commercialisation.
“The interest in regard to decommissioning is operators who see themselves as delay asset management companies and want to change or look at game changers to reduce the cost of decommissioning,” Vollmar remarked.
“There is also interest beyond decommissioning in production enhancement, for example. As the oil and gas prices increases, we need to look at solutions which reduce costs and simplify the process. Usually, you can collect wells with the same well challenges which only require wireline (for example) for a campaign. Then you need to get a certain threshold to justify the costs to mobilise other equipment. Our approach gives you the advantage as it is multipurpose and has all this included. You can combine now all the different well interventions and justify the cost much easier, which obviously increases the recovery factor of mature fields.” The wide application range simplifies wireline, side track drilling, coiled tubing, ESP runs, conductor pulling, life well interventions or slot recovery operations. On top, the dual jacking system reduces operational time by almost 40% and its offering a hoisting capacity up to 250mt.
For the next steps on its promising journey, Voll Marintek will be conducting a FEED study in September 2022 for which they have been granted a significant grant by Innovate UK. The company will look at different potential well designs which would require P&A and test the technical, commercial and operational feasibility of the Lean Machine against them. Over the course of the study, further engineering and optimisation of the solution will be undertaken.
“We are already receiving interest from operators to manufacture the system and offer it at a rental rate. The idea here would be we manufacture the system, rent it out and then provide maintenance and support when needed,” surmised Vollmar.
While Europe is the launch pad, it is clear that Vollmar has no intention of shackling his ambitions to this region, but instead envisioned the Lean Machine being rolled out across the globe.
“This solution has been developed through niche market research and I looked at a lot which are not currently provided for with a sufficient solution. For example, Australia and Brunei have a lot of wells in four to five metres water depth which you cannot enter with normal jackups. So you need to engineer something which is light, compact and could be added to any vessel of opportunity. But, at the same time, you don’t want to make any large vessel modification. So companies have been looking at lift barges to put a cantilever on but this is not economical or would only be so with a contract for 5-10 years as, again, you need to make modifications. It would be much easier to have something light and compact which could be put on top of the wellheads and even deployed by a jacking barge (or between two).”
“In Asia and Africa, people did not really think about workovers and so you often find wells with a production facility incredibly close. Workover equipment is only feasible if you look really deeply into interfaces and have the time and resources to do it. The Lean Machine could really help here and can be easily adapted depending on how much space is available at location.”
While it was clear that Vollmar is very much ready to take on the world with the Lean Machine, for now it is time to build the foundations. After the start of the FEED study, the next steps for Voll Marintek will be building alliances, manufacturing and testing and field trials before commercialisation – currently targeted in 2024/25. Without doubt, however, there will be many in the industry following this progression with great interest.




