 Exergy International and Geothermal Engineering Ltd. (GEL) have signed a contract for the supply of a 3MWe gross capacity Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) power plant in Cornwall.
Exergy International and Geothermal Engineering Ltd. (GEL) have signed a contract for the supply of a 3MWe gross capacity Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) power plant in Cornwall.
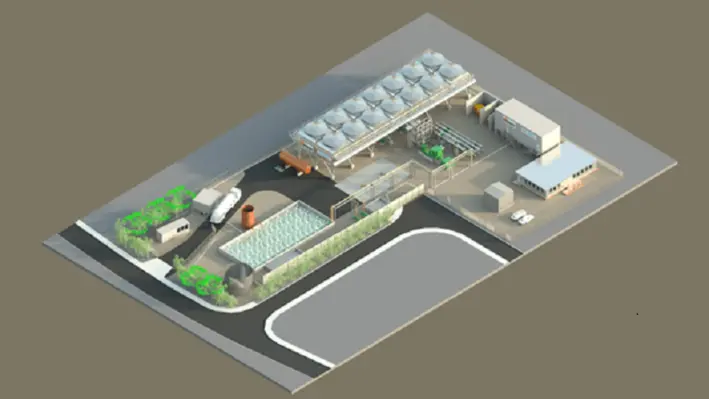
The United Downs project represents the first integrated deep geothermal project in the UK, poised to produce 3MWe of baseload power and up to 10MWth of zero-carbon heat for the large housing development at Langarth Garden Village.
The turnkey EPC contract awarded to Exergy covers the design and engineering to the ORC system, the manufacturing of the equipment and the overall build of the power plant. As the system will be a closed loop cycle, the plant will not release any vapour into the atmosphere and will boast a small footprint with a minimal visual impact.
The system will be delivered over 18 months, with the commissioning process expected by late 2024. Once in operation, the installation is predicted to save more than 6,500 tonnes of CO2 emissions per year.
Luca Pozzoni, General Manager of Exergy International, said, “We are excited to embark on this journey with GEL. The United Downs project will be a milestone in the development of the geothermal industry in the UK and will give us the valuable opportunity to contribute with our technology and expertise to kick-starting geothermal power generation in the country.”
CEO of GEL, Ryan Law, commented, “Geothermal heat is an untapped renewable resource with the potential to provide huge amounts of energy-efficient and carbon-free electricity and heat. Exergy is well known globally for their competence in the binary geothermal power sector and we are very pleased to be working with them on this landmark project in Cornwall.”
The United Downs Deep Geothermal Power project will be home to the first deep geothermal power plant in the UK. Two directional wells have already successfully been drilled for purpose, with production well being measured to a depth of 5,275 m – the deepest onshore well in the UK – and the injection well to 2,939 m.

 International well plug and abandonment specialists, Well-Safe Solutions, are expanding into the Asia Pacific region with the appointment of Massimo Delia as General Manager of the newly created Well-Safe Solutions Pty Ltd.
International well plug and abandonment specialists, Well-Safe Solutions, are expanding into the Asia Pacific region with the appointment of Massimo Delia as General Manager of the newly created Well-Safe Solutions Pty Ltd.
Based in Perth, Australia, Massimo joins the company with more than 20 years of subsea commercial and engineering experience.
Commenting on his appointment, Massimo said, “I have watched Well-Safe Solutions go from strength to strength in Europe, with the growth of its Subsurface and Well Engineering team capabilities and the mobilisation of all three well plug and abandonment assets for the first time in the company’s history being just some of the recent highlights.
“I am eager to play my part in the next chapter of the company’s growth and look forward to collaborating with my colleagues, clients and stakeholders in the UK and Australia.”
Phil Milton, Chief Executive Officer of Well-Safe Solutions, said, “Working in tandem with the wider Well-Safe Solutions team, Massimo will be instrumental in leveraging our capabilities and track record to partner with operations and stakeholders throughout Australia and Asia.
“We’re looking forward to undertaking offshore and onshore well decommissioning projects with the input of the highly experiences engineering sector and supply chain already present within the region.”
In the initial assessment of Australia’s offshore oil and gas decommissioning liabilities, the Centre of Decommissioning Australia (CODA) has identified more than US$50bn worth of work ahead – with well P&A and pipeline removal the majority of the estimated spend. This includes the abandonment of more than 1,000 offshore wells, in addition to a significant onshore market.
With more than 400 wells worldwide featuring Well-Safe Solutions’ engineering expertise and more than 70 wells either decommissioned or to be decommissioned by the business in the North Sea alone, the company is well-placed to deliver on its mission to provide safe, efficient and collaborative well plug and abandonment operations in the Asia Pacific region.

 Fervo Energy, one of the leaders in next-generation geothermal technology, has announced the successful completion of its well test at its full-scale commercial pilot project, Project Red, in Nevada.
Fervo Energy, one of the leaders in next-generation geothermal technology, has announced the successful completion of its well test at its full-scale commercial pilot project, Project Red, in Nevada.
The successful test confirmed the commercial viability of Fervo’s drilling technology and further established Project Red as one of the most productive enhanced geothermal systems (ESG) to date. The 30-day well test achieved a flow rate of 63 litres per second at high temperature, which enabled 3.5MW of electric production, setting new records for both flow and power output from an EGS.
Fervo is the first company to successfully drill a horizontal well pair for commercial geothermal production, achieving lateral lengths of 3,250 ft, and reaching temperatures of 191°C. Data collected through the course of this pilot prohject will enable rapid advancement in geothermal deployment, with Fervo’s next horizontal well pair planned to achieve more than double the power output of the pilot design.
Tim Latimer, Fervo Energy CEO and Co-Founder, said, “By applying drilling technology from the oil and gas industry, we have proven that we can produce 24/7 carbon-free energy resources in new geographies across the world. The incredible results we share today are the product of many years of dedicated work and commitment from Fervo employees and industry partners, especially Google.”
Fervo and Google signed the world’s first corporate agreement in 2021 to develop next-generation geothermal power. The end goal for the partnership is to power Google’s Cloud region in Las Vegas with an ‘always-on’, carbon-free resource that will reduce the company’s hourly reliance on fossil fuels.
Results from Project Red indicate that geothermal energy could supply more than 20% of US power needs and compliment wind and solar in order to reach a fully decarbonised grid.


Allseas has awarded Modern American Recycling Services Europe (MARS) with the contract for project management and engineering, receipt with load-in assistance, dismantling and disposal of EnQuest’s Heather Alpha topsides.
The contract was announced on MARS’ social media platforms, and will provide the chance for the company to participate in the decommissioning of the 13,000 t topsides.
As part of the project, EnQuest will make use of Allseas’ Pioneering Spirit, a 48,000t offshore construction vessel that is designed for single-lift installation and removal of offshore platforms as well as the installation of record-weight pipelines. The ship has proven its ability to lift entire topsides of up to 48,000 t and jackets up to 20,000 t in a single piece.
The vessel will be used to remove the Heather topsides in a single lift operation. Preparations for the lift will begin next year, with the lift itself scheduled for 2025.
Following this work, in subsequent years, M.A.R.S. will recycle the platform in compliance with international, national and local rules and regulations.

 As operators are racing to keep their heads above water as the energy transition continues to grow in momentum, instability in energy security is adding fuel to the fire and putting Europe’s energy market in jeopardy. Following the turbulent oil market over the past three years and the sanctions issued against Russia, heads are beginning to turn to geothermal to meet the rising demand for heating systems across the continent.
As operators are racing to keep their heads above water as the energy transition continues to grow in momentum, instability in energy security is adding fuel to the fire and putting Europe’s energy market in jeopardy. Following the turbulent oil market over the past three years and the sanctions issued against Russia, heads are beginning to turn to geothermal to meet the rising demand for heating systems across the continent.
Scaling geothermal heating sources in Europe could fundamentally provide not only a big stepping stone for meeting environmental targets, but also implement a more established level of energy security regionally. For the first time, policymakers are integrating geothermal movements into frameworks and governments across the continent are increasing funding for pilot projects.
The geothermal scene is hotting up, however, a number of challenges are still holding the industry back from reaching its full potential. High financial barriers appear too big to scale with the current resources available, with international players hesitant to invest in the European market. Collaboration between geothermal experts and the oil and gas community is key to bridging the gaps presented in the market and could be the key component to utilising geothermal energy to ensure energy security.
Read Offshore Network’s full report here to understand the current state of play within the European geothermal industry and hear from experts as they share their insights into how the market can receive the boost it needs to ensure regional environmental targets are met and that energy security is assured.


Relatively stable oil prices and a growing global oil demand is creating favourable dynamics for the oil and gas community in the near-future, however uncertainty is rife over how long this will last as the race to meet the Paris Agreement 2050 target intensifies.
While this is raising questions over further drilling activity offshore Australia, it is suggesting a promising future for the country’s well intervention market as operators seek to squeeze the last drops of oil out of existing assets and perform end-of-life work in preparation for the substantial decommissioning task ahead. At the same time, the offshore carbon capture and storage space is garnering significant interest and marks another tantalising frontier that is receiving Government backing.
Read Offshore Network’s full report to understand the background and nuances of Australia’s offshore well intervention market as well as the potential challenges (such as labour shortages and vessel availability) which threatens to stifle it.

 McDermott has been awarded an engineering, procurement and removal contract for offshore decommissioning work by Woodside Energy.
McDermott has been awarded an engineering, procurement and removal contract for offshore decommissioning work by Woodside Energy.
The award is for the full removal of the Stybarrow disconnectable turret mooring (DTM) buoy, as part of the decommissioning of the Stybarrow field located in the north-western Cape of Western Australia.
Under the contract scope, McDermott will provide project management and engineering services for the recovery, transportation and offloading of the DTM buoy to an onshore yard for dismantling and disposal.
Mahesh Swaminathan, Senior Vice President, Subsea and Floating Facilities, McDermott, said, “This award not only demonstrates McDermott’s proven track record in undertaking deepwater projects of diverse scopes, but it also highlights the critical importance of decommissioning in the offshore industry.
“With our seamless integration of engineering, fabrication, and offshore mobilisation expertise, we believe we are well-equipped to execute this project efficiently and responsibly, ensuring the safe recovery and removal of the Stybarrow DTM buoy.”
The DTM buoy will be removed utilising McDermott’s DLV2000 vessel, with the Perth-based team overseeing project management while engineering and fabrication support will be provided by the team in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and Batam, Indonesia.

 Global energy consultancy Xodus has been awarded a contract to provide technical and project support services for Phase One of the decommissioning of the Northern Endeavour FPSO.
Global energy consultancy Xodus has been awarded a contract to provide technical and project support services for Phase One of the decommissioning of the Northern Endeavour FPSO.
Phase One covers activities to facilitate the disconnection and removal of the FPSO including topsides and subsea flushing and well suspension.
Xodus will be working on behalf of the Australian Government, providing advice and project coordination, regulatory and environment, health and safety, technical, quality assurance, and contract management as part of the agreement.
Alasdair Gray, Late Life and Decommissioning Lead at Xodus, said, “We have a highly experienced local team with several of our colleagues having extensive experience of the Northern Endeavour either from the early design and installation phase of the project or during production operations. This means that whilst being able to bring a fresh approach, the facility is already familiar to much of the team.
“We understand environmental sensitivities and the impact these can have on any proposed activity or execution plan. Expert technical advice and careful planning will be critical to the successful decommissioning of the offshore field in a safe and responsible manner. We are pleased to provide the necessary support to ensure that the decommissioning strategy is robust and ultimately compliant with regulatory expectations.”
The Northern Endeavour is a 274 m long FPOS which is permanently moored between the Laminaria and Corallina oil fields in the Timor Sea. The now redundant production system comprises a network of subsea wells tied back to the permanently moored vessel unit through a system of subsea manifolds, flowlines, umbilicals, and dynamic risers.


Trendsetter Engineering, a provider of specialised subsea hardware and offshore service solutions from exploration drilling through to abandonment, has announced the recent completion of two deepwater well stimulation campaigns for major operators in the Gulf of Mexico.
The two campaigns resulted in the successful acid treatments of a combined six wells. The campaigns arrived on the heels of a contract agreement to deliver hydraulic intervention and technical services via the Subsea Tree Injection Manifold (STIM) for a Hydrate Remediation and Flowline Flush Project in the Gulf of Mexico.
The Trendsetter STIM offers a 15,000psi rated subsea safety system designed to provide hydraulic well access for both vertical and horizontal tree types. In addition to hydraulic well stimulation, the STIM unit has been used and is capable of supporting various other hydraulic intervention operations including hydrate remediation, bull heading of kill weight fluid and cement as well flowline flushing and testing operations for both pre and decommissioning.


According to Rystad Energy, the well intervention market is receiving a healthy boost as oil and gas companies look to increase their output.
The research and business intelligence company claimed that spending on interventions is projected to jump by almost 20% in 2023 to total US$58bn and this is just the start of a surge in the coming years.
The intervention rate is forecast to reach 17% in 2027 which would total about 260,000 wells globally.
Breaking this down, Rystad showed that more than US$11bn of the total expenditure will be directed to the wireline & perforating segment, while together, intervention units and oilfield chemicals sectors will represent 35%. In addition, the sum of the investments in coiled tubing, water management, and intervention tools is expected to close 2023 surpassing US$20bn.
Regionally, onshore interventions in Asia, South America, and Africa will lead the 9% growth in activities related to intervention during 2024, a year expected to be significant for the well intervention market. North America is projected to account for 64% of the total oil and gas wells ready for intervention in 2027, whereas Asia and South America will reach their maximum in 2026, with respectively 41,413 and 9,703 wells.
Jenny Feng, Supply Chain Analyst at Rystad Energy, explained, “As oil demand picks up in the second half of this year, operators will look to ramp up production from existing fields, and well interventions will be a vital piece of the puzzle. As a quick, efficient, and cost-effective method of maximizing existing resources, interventions are going to be a hot topic in the years to come.”
In terms of offshore markets, 618 assets are highly attractive for intervention. Norway and Australia stand out with 36% and 25%, respectively, while the UK has 91 wells likely to be involved in intervention activities.



Decom Engineering (Decom) has invested more than UK£1mn to develop its largest chopsaw to date.
The C1-46 Chopsaw has been delivered in response to client demand for larger sized subsea pipe-cutting capability. It is designed to cut tubulars and other materials up to 46” and is able to cut a wide range of materials, including inconel alloys, duplex and concrete.
With the ability to cut in any orientation, the C1-46 is capable of multiple cuts per blade (20-100), resulting in large cost savings and increased efficiency. Blade changes are efficient, safe and the chopsaw can be supplied set up in a number of configurations and settings to suit project requirements.
It can be operated in water depths of up to 2,000 m and is currently deployed on its first project on behalf of a global energy company on a UK North Sea workscope.
The solution is able to achieve a versatile angle of deployment and an array of cuts can be completed whilst subsea or held in wet storage, without returning to the surface. The Tungsten Carbide Tipped saw, which can be operated topside or by ROV (with hot stab capability), is highly adaptable to suit challenging surroundings and varied structures.
Decom Engineering Managing Director, Sean Conway, commented, “Our commitment to research and development is a differentiator and making this significant investment to bring the C1-46 Chopsaw to market was a result of clients indicating they would welcome larger sized cutting options, as this is an area existing technologies struggle with.
“Decom are focused on supporting clients in solving their problems by asking how we can do more. This flagship product is designed for large subsea cutting operations and can cut through tough exotic materials and thick coatings with ease, while maintaining clean cuts for easy access to flush pipelines or recycle pipes.
“The saw clamps are designed to penetrate into the sea bed/sediment and to minimise the need for trenching. We are excited to see the C1-46 perform successfully on this North Sea project and we will take the lessons learned to refine and improve the product and its operational capabilities.
“Given the strong track record of success with our other models of the C1 Chopsaw we are confident that this latest version will perform well and will meet client expectations but we are always looking for ways to improve our offering.”



Valaris has secured new contracts and contract extensions to leave its associated contract backlog at approximately US$150mn.
The new scope includes:
• A two-well contract with Anadarko Petroleum Corporation in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico for semisubmersible VALARIS DPS-5. The contract is expected to commence in July 2023 and has a minimum duration of 60 days.
• A nine-well contract for a plug and abandonment campaign with Apache in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico for semisubmersible VALARIS DPS-5. The contract is expected to commence in September 2023 and has a minimum duration of 110 days.
• A minimum duration 180-day contract with an undisclosed operator offshore Australia for heavy duty modern jackup VALARIS 107. The contract is expected to commence in first quarter 2024.
• A one-year contract with an undisclosed operator offshore Australia for heavy duty modern jackup VALARIS 107. The contract is expected to commence in October 2024.
• A two-well contract with a major Australian operator for heavy duty ultra-harsh environment jackup VALARIS 247. The contract is expected to commence in early to mid-2024 and has an estimated duration of 100 days.
Page 67 of 118